62.146.66.187 personal.avira-update.com personal.avira-cdn.com
80.190.143.232 personal.avira-update.net
80.190.143.229 perspeak.avira-update.comChủ Nhật, 2 tháng 12, 2012
Fix error "Can't Update Avira 12"
Go to the host file and add this.
Chủ Nhật, 7 tháng 10, 2012
Phim tắt vào Bios Sony Vaio, HP, Lenovo, Dell Acer, Asus
SONY VAIO
Vào Bios ------- nhấn F2
Recovery --------nhấn F10
Để boot vào đĩa CD/DVD thì các bạn cho đĩa vào ổ đĩa rồi khởi động lại máy, máy sẽ tự động boot vào ổ đĩa.(vì dòng SONY mạc định là boot ổ CD/DVD đầu tiên rồi).
HP – Compaq
Vào Bios ------nhấn F10
Chọn boot - ---nhấn F9
Recovery--- ---nhấn F11
Lenovo Thinkpad
Vào Bios--------nhấn F1
Chọn boot-------nhấn F12
Recovery--------nhấn phím xanh ThinkVantage
Dell
Vào Bios-------nhấn F2
Chọn boot-------nhấn F12
Recovery----------nhấn F8 rồi chọn Repair your Computer
Acer
Boot của Acer là F12 + vào bios F2 (thường chức năng menu boot bị disible phải vào enale mới bấm F12 được)
Asus
Boot của Asus là ESC + vào Bios là F2
Vào Bios ------- nhấn F2
Recovery --------nhấn F10
Để boot vào đĩa CD/DVD thì các bạn cho đĩa vào ổ đĩa rồi khởi động lại máy, máy sẽ tự động boot vào ổ đĩa.(vì dòng SONY mạc định là boot ổ CD/DVD đầu tiên rồi).
HP – Compaq
Vào Bios ------nhấn F10
Chọn boot - ---nhấn F9
Recovery--- ---nhấn F11
Lenovo Thinkpad
Vào Bios--------nhấn F1
Chọn boot-------nhấn F12
Recovery--------nhấn phím xanh ThinkVantage
Dell
Vào Bios-------nhấn F2
Chọn boot-------nhấn F12
Recovery----------nhấn F8 rồi chọn Repair your Computer
Acer
Boot của Acer là F12 + vào bios F2 (thường chức năng menu boot bị disible phải vào enale mới bấm F12 được)
Asus
Boot của Asus là ESC + vào Bios là F2
ARP Cache
What is the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)?
ARP or the Address Resolution Protocol is primarily used to connect the OSI Model Network Layer (Layer 3) to the Data Link Layer (Layer 2). For most networks this refers to the linking of IP addresses to MAC addresses in Ethernet addressing. For a computer or other networking capable device to be able to communicate with another, the Ethernet MAC address must be known. If the desired recipient of the transmission is located outside of a LAN, the router or default gateway’s MAC address must be known for the computer to send outgoing messages.How Does ARP Cache Work?
ARP cache makes use of two types of entry: static and dynamic. The majority of the time, dynamic ARP cache entries are made. For the dynamic scheme, the ARP entry (the MAC address to IP address mapping) is kept on the computer or networked device for a set amount of time (normally for the length of time that it is being used). For static entries, the mapping is manually entered representing the Ethernet MAC to IP address mapping. Due to the management overhead required with static entries, dynamic ARP is primarily used in modern computing equipment.A dynamic ARP entry is created by using the ARP protocol. Once a website or host is resolved to an IP address using a DNS server, the computer will send an ARP request. The message is sent to the LAN first requesting the Ethernet MAC address for the desired IP address. If located on the local LAN, the computer or server with the IP address will respond with the corresponding MAC address which is entered into the requesting devices ARP cache. The entry will remain until not being used or the ARP cache times out. Routers also maintain their own ARP cache. The ARP cache for a switch will also store the MAC addresses connected to respective ports on the switch.
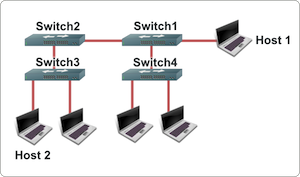
How Do You Display the ARP Cache?
Display ARP Cache in WindowsStep 1 – Open the Windows command prompt by selecting the “Start” menu button and entering “command” in the search text field.
Step 2 – Type “arp –a” followed by pressing the “Enter” key to view the ARP cache displayed on the DOS console.
C:>arp -a
Interface: 192.168.1.101 — 0×80004
Internet Address Physical Address Type
192.168.1.1 00-0d-6d-bc-a8-6b dynamic
192.168.1.2 00-0e-1c-2b-e5-3c dynamic
Display ARP Cache in Unix
Step 1 – Open the Unix console.
Step 2 – Enter “arp –a” followed by pressing the “enter” or “return” key on your computer’s keyboard and view the ARP cache contents subsequently displayed.
$ arp -a
www.tech-faq.com (192.168.1.2) at 00:34:c4:45:73:21 on fxp0 permanent [ethernet]
fw.tech-faq.com (192.168.1.1) at 00:34:62:a1:c2:00 on fxp0 [ethernet]
What Are the Benefits of ARP Cache?
ARP cache helps save computer and networking resources by saving the MAC to IP address mapping required for network communication. As a result, it is an enabler for the Address Resolution Protocol by further accelerating the methods of locating host hardware addresses when the network layer is known through DNS lookup.What Are the Symptoms of a Faulty ARP Cache?
With time, ARP cache entries can become stale. It is possible for additional entries to the ARP cache table to be made without removing expired entries from the stored table. Eventually, this will result in errors that can significantly impact computer or network performance. Some of the symptoms seen when the ARP cache requires clearing include web pages that fail to load and the failure to ping various IP addresses.How to Clear ARP Cache in Windows XP, Vista, and 2K
Clear ARP Cache from the MS DOS PromptStep 1 – Login to your computer with an account that has administrator permissions.
Step 2 – Select the “Start” menu button. On Windows XP and Windows 2K select the “Run” menu option. Then enter “cmd” or “command” in the run text box followed by clicking the “enter” key. On Windows Vista and newer versions of the OS enter the word “command” in the search text field followed by pressing the “enter” key.
Step 3 – Enter “netsh interface ip delete arpcache” at the command prompt and press the “enter” key.
Step 4 – Wait for approximately 30 seconds to 20 minutes based on the size of the ARP cache table and speed of your computer for the dynamic ARP cache to be cleared.
Clear ARP Cache from Windows Control Panel
In the event you are not able to clear ARP cache from the DOS prompt or just are not comfortable conducting command line tasks, it is possible to clear ARP cache on the Windows OS from Windows Control Panel.
Step 1 – Select the “Start” menu button followed by choosing the “Control Panel” icon.
Step 2 – Depending on the version of Windows OS on the computer and the “view type” selected for Windows Control Panel, you may or may not need to choose the “Performance and Maintenance” menu option.
Step 3 – Choose the “Administrative Tools” menu option followed by the “Computer Management” menu choice.
Step 4 – Select the “Services and Applications” menu button located on the right-hand side of the screen.
Step 5 – Scroll down the menu options until you locate the “Routing and Remote Services” menu option.
Step 6 – Choose the “Routing and Remote Services” menu tab and a dialogue window will then open.
Step 7 – Select the drop-down menu and choose the “Disabled” option followed by clicking the “Ok” menu button to save the settings and clear the ARP cache.
Step 8 – Restart your computer and enabled the “Routing and Remote Services” menu option selected in step 7 to complete clearing the ARP cache.
How to Clear the APR Cache in Windows 7/Server 2003/2008
Step 1 – Select the “Start” menu button and enter “command” in the search text field followed by pressing the “enter” key.Step 2 – Input the following command at the MS DOS command prompt, “netsh interface ip delete arpcache” and press the “enter” key.
Step 3 – Wait for between 1 – 20 minutes for the ARP cache table to be deleted based on the version of OS installed on the computer. Windows Server 2003/2008 will normally take greater than 10 minutes to complete the task due to storing larger cache tables. Windows 2007 will normally complete the task in under 1-2 minutes.
How to Delete an IP Address from ARP Cache
Step 1 – Open the MS DOS prompt on the computer.Step 2 – input “arp –d <IP address>” with the brackets not being included on the address to remove from ARP cache. For example, arp –d 10.1.1.2 will remove the 10.1.1.2 entry from the ARP table.
Step 3 – Display the ARP table after deleting an entry by entering, “arp –a” at the MS DOS command prompt.
Step 4 – Add a static entry to the ARP table by entering the following command at the MS DOS command prompt, “arp -s <ip address> <mac address>.” An example of a static ARP entry is:
arp -s 157.55.85.212 00-aa-00-62-c6-09
What Do You Do if Clearing ARP Cache Fails?
Clearing ARP cache on a computer running the Microsoft Windows OS can fail due to bugs or conflicts within the OS. When the cache fails to clear, the OS will provide the following message to the end-user:Windows could not finish repairing the problem because the following operation could not be completed:
Clearing the ARP cache
For assistance, contact the person who manages your network
The error is typically thrown with the Windows Routing and Remote Services application is enabled or turned on. For most end-users, this service is not required to be enabled and can be turned off to troubleshoot ARP cache clearing issues.
Step 1 – Select the “Start” menu button and click the “Control Panel” icon.
Step 2 – Change the Control Panel view to “Classic” if currently set to “Category View” and select the “Administrative Tools” menu option.
Step 3 – Select the “Computer Management” menu choice and then double click the “Services and Applications” menu option.
Step 4 – Double click the “Services” menu option and scroll to the “Routing and Remote Services” menu label.
Step 5 – Double click the “Routing and Remote Services” menu button and locate the “Startup Type” field.
Step 6 – Change the option selected to “Disabled” and ensure the service status reflects “Stopped.” If it has not ceased to run, click the “Stop” menu button.
Step 7 – Click the “Ok” menu button and retry clearing ARP cache on your computer.
Thứ Ba, 18 tháng 9, 2012
Định dạng USB chuẩn NTFS
Nếu USb là ổ G
CMD
convert g: /fs:ntfs /v
Nếu báo lỗi thì thêm
CMD
chkdsk g: /f
convert g: /fs:ntfs /v
CMD
convert g: /fs:ntfs /v
Nếu báo lỗi thì thêm
CMD
chkdsk g: /f
convert g: /fs:ntfs /v
Thứ Bảy, 28 tháng 7, 2012
Linux Networking Setup
Required InformationTo enable networking, you must configure your network interface card or cards with an IP address and netmask. The kernel must have support for your cards compiled in, either as modular support or direct support. If you don't have kernel support read the sections about the kernel and how to compile it. To set your cards up, do the following. In my example my network is 192.168.1.0, IP=192.168.1.100, broadcast=192.168.1.255, netmask=255.255.255.0, gateway-192.168.1.1, nameserver=192.168.1.10.
|
Configuration tools
There are many network configuration tools today. They are:| netconf | A GUI interactive interface available on Redhat 6.1 | |
| linuxconf | A GUI interactive interface available on Redhat 6.1 which includes netconf configuration. | |
| netconfig | A GUI step by step interface | |
| ifconfig | A text based program to configure the network interface. Type "man ifconfig" for info. |
- /etc/sysconfig/network - Defines your network and some of its characteristics.
- /etc/HOSTNAME - Shows the host name of this host. IF your name is "myhost" then that is exactly the text this file will contain.
- /etc/resolv.conf - Specifies the domain to be searched for host names to connect to, the nameserver address, and the search order for the nameservers.
- /etc/host.conf - Specifies the order nameservice looks to resolve names.
- /etc/hosts - Shows addresses and names of local hosts.
- /etc/networks - Provides a database of network names with network addresses similar to the /etc/hosts file. This file is not required for operation.
- /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth* - There is a file for each network interface. This file contains the IP address of the interface and many other setup variables.
Analysis Tools
- netstat - Displays information about the systems network connections, including port connections, routing tables, and more. The command "netstar -r" will display the routing table.
- traceroute - This command can be used to determine the network route from your computer to some other computer on your network or the internet. To use it you can type "route IPaddress" of the computer you want to see the route to.
- nslookup - Used to query DNS servers for information about hosts.
- arp - This program lets the user read or modify their arp cache.
- tcpdump - This program allows the user to see TCP traffic on their network.
- dig(1) - Send domain name query packets to name servers for debugging or testing.
Manual Configuration
You can use one of the above tools or configure the network the old fashioned way as follows:- First to use networking on any permanent basis you should setup the file /etc/sysconfig/network similar to the example shown below.
- Assign an ip address with "ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.100 netmask 255.255.255.0 up".
- Tell your machine that a hub is ready for information with the command "route add -net 192.168.0.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 eth0"
- To contact hosts outside your network if a machine with IP address 192.168.1.1 is the gateway use the command "route add default gw 192.168.1.1 eth0"
- If using a dialup connection use the command "route add default
ppp0" The word default says if the packet is not for a machine on your
local network, send it to the default device.
DEVICE="eth0" IPADDR="192.168.1.100" NETMASK="255.255.0.0" ONBOOT="yes" BOOTPROTO="none" IPXNETNUM_802_2="" IPXPRIMARY_802_2="no" IPXACTIVE_802_2="no" IPXNETNUM_802_3="" IPXPRIMARY_802_3="no" IPXACTIVE_802_3="no" IPXNETNUM_ETHERII="" IPXPRIMARY_ETHERII="no" IPXACTIVE_ETHERII="no" IPXNETNUM_SNAP="" IPXPRIMARY_SNAP="no" IPXACTIVE_SNAP="no"Unless you know what you're doing it is best to use a network configuration tool. I cannot guarantee the accurateness of how to set these files up on your system.
Configuring an interface for multiple IP addresses
If you want to configure your network card to act as more than one IP address, issue the following command:
ifconfig dummy 192.168.1.102 netmask 255.255.255.0
This uses the dummy system interface capability supported in the kernel
to setup another virtual interface which operates at IP address
192.168.1.102. Substitute the IP address that you want your virtual
interface to be with an appropriate netmask for your network. To
disable this, issue the following command.
ifconfig dummy down
Another way to use multiple IP addresses on one ethernet card is to set
up a new file in your /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory. Copy
your ifcfg-eth0 role to ifcfg-eth0:0. Edit that file and rename the
device to "eth0:0" and the IP address to the desired IP address. You
may also want to modify BROADCAST, NETWORK, or NETMASK. You can
continue adding IP addresses by using :1, :2, etc such as ifcfg-eth0:2.To make it effective, you must reboot your system or issue the command "/etc/rc.d/init.d/network restart" as root.
Dynamically allocated IP addresses
To get the IP address of a dynamically allocated network interface in a script file enter the following:
dynip=`/sbin/ifconfig | grep -A 4 ppp0 | awk '/inet/ { print $2 } ' | sed -e s/addr://`
Substitute the correct interface that you get your dynamic IP address in
for ppp0 in the example above. This script line gets your dynamic IP
address for use in a masquerade script. You can use the variable $dynip
as in any other configuration. The next time you make a new
connection you will need to extract the dynip value again and re-run the
masquerade script.
Networking file formats, examples and considerations
Below are listed some more in depth information about the networking files.- /etc/sysconfig/network
The /etc/inittab file contains the entry "si::sysinit:/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit" which causes the system at startup to run the rc.sysinit script. The rc.sysinit file expects to find the file /etc/sysconfig/network if networking is to be enabled.
The network file looks like this:NETWORKING=yesWhere GATEWAYDEV is the network interface card that is attached to the network the gateway machine is on. The GATEWAY is the actual IP address of the gateway machine.
FORWARD_IPV4=false
HOSTNAME=mymachine.mycompany.com
DOMAINNAME=mycompany.com
GATEWAY=192.168.1.1
GATEWAYDEV=eth0
- /etc/hosts - Defines local hosts.
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain 192.168.1.100 mymachine.mycompany.com mymachine
- /etc/services - Internet network services list. It associates port numbers with names of services. The file contains three fields which are name, port/protocol, and aliases with an optional comment.
- /etc/protocols - Describes DARPA internet protocols available
from the TCP/IP subsystem. Maps protocol ID numbers to protocol names.
It includes protocol name, number, and aliases. The protocol file on
my system:
# /etc/protocols: # $Id: protocols,v 1.1 1995/02/24 01:09:41 imurdock Exp $ # # Internet (IP) protocols # # from: @(#)protocols 5.1 (Berkeley) 4/17/89 # # Updated for NetBSD based on RFC 1340, Assigned Numbers (July 1992). ip 0 IP # internet protocol, pseudo protocol number icmp 1 ICMP # internet control message protocol igmp 2 IGMP # Internet Group Management ggp 3 GGP # gateway-gateway protocol ipencap 4 IP-ENCAP # IP encapsulated in IP (officially ``IP'') st 5 ST # ST datagram mode tcp 6 TCP # transmission control protocol egp 8 EGP # exterior gateway protocol pup 12 PUP # PARC universal packet protocol udp 17 UDP # user datagram protocol hmp 20 HMP # host monitoring protocol xns-idp 22 XNS-IDP # Xerox NS IDP rdp 27 RDP # "reliable datagram" protocol iso-tp4 29 ISO-TP4 # ISO Transport Protocol class 4 xtp 36 XTP # Xpress Tranfer Protocol ddp 37 DDP # Datagram Delivery Protocol idpr-cmtp 39 IDPR-CMTP # IDPR Control Message Transport rspf 73 RSPF #Radio Shortest Path First. vmtp 81 VMTP # Versatile Message Transport ospf 89 OSPFIGP # Open Shortest Path First IGP ipip 94 IPIP # Yet Another IP encapsulation encap 98 ENCAP # Yet Another IP encapsulation
- /etc/named.conf - Used for domain name service to configure named. Other files used are dependent on this file. This file is explained further in the DNS section
- /etc/resolv.conf - Specifies the domain to be searched for host
names to connect to, the nameserver address, and the search order for
the nameservers.
domain mycompany.com search mycompany.com mynet.net nameserver 192.168.1.100 nameserver 192.168.199.1 nameserver 192.168.1.10
The third line specifies that DNS should be tried on my machine first then use the normal nameserver on the fifth line. The fourth line specifies that my machine is running nameservices on another network which is using interface 192.168.199.1. This assumes the nameserver is set up on my machine which is explained in another section.
- /etc/host.conf - Specifies the order nameservice looks to resolve names. An example file:
order hosts, bind multi on nospoof on
The order specifies that when resolving names to first look in the /etc/host file, then use BIND8 (DNS) to resolve the name. The line "multi on" specifies that all valid addresses for a host found in the hosts file should be returned.
Older X windows configuration
In Xwindows a working configuration is set up as follows:- NAMES:
- hostname: mymachine.mycompany.com
- Domain: mycompany.com
- Nameservers: 192.168.1.10
- HOSTS:
- IP - 192.168.1.100
- Name - mymachine.mycompany.com
- INTERFACES:
- Interface - eth0
- IP- 192.168.1.100
- proto - none
- atboot - yes
- Netmask: 255.255.255.0
- Network: 192.168.1.0
- Broadcast: 192.168.1.255
- ROUTING:
- Default gateway: 192.168.1.1
- Default gateway device: eth0
- Interface - 192.168.1.100
- Network Address - 192.168.1.0
- Network gateway 192.168.1.1
- Netmask - 255.255.255.0
Routing
Routing table information is used to route incoming and outgoing network diagrams to other machines. On most simple configurations, there are three routes. One for sending packets to your own machine, one for sending packets to other machines on your network and one for sending packets to other machines outside your network through the gateway. Two programs (ifconfig and route) are used to configure these parameters. They are described in more detail in the routing section.Enable SSH in ESX Server
Login by user Root, after that, use command:
- perl -spi -e 's/PermitRootLogin no/PermitRootLogin yes/'
/etc/ssh/sshd_config
- esxcfg-firewall -e sshClient
- service sshd restart
Changing the IP address, default gateway, and hostname of the Service Console in ESX
Details
This article provides steps to change the Service Console IP address, gateway address, and hostname on an ESX 3.x and 4.x host.
Solution
Note:
ESX 4.0 Update 2 introduces a new tool that simplifies the process of
creating or restoring networking in the ESX service console. For more
information, see Configuring or restoring networking from the ESX service console using console-setup (1022078).
Note: To change the IP network information on an ESXi host, see Configuring the ESXi Management Network from the direct console (1006710)
Configuring the ESXi Management Network from the direct console (1006710)
.
Note: If the changed IP does not persist across a reboot, try deleting and recreating the Service Console vswif management interface. For more information, see Recreating Service Console networking from the command line (1000266).
Note: This command creates a temporary hostname change. This change is lost when the system is rebooted.
Each time you restart the vmware-hostd process, the mgmt-vmware script searches for existing certificate files (
To generate new certificates:
Note: To change the IP network information on an ESXi host, see
 Configuring the ESXi Management Network from the direct console (1006710)
Configuring the ESXi Management Network from the direct console (1006710).
Changing settings from the physical or remote console connection
Changing the IP for the Service Console must be done from the physical console or through a remote console session. If you make changes through a network connection such as SSH, network connectivity to the Service Console disconnects because the Service Console's network interface changes.- Run this command to set the IP address:
[root@server root]# esxcfg-vswif -i a.b.c.d -n w.x.y.z vswif0wherea.b.c.dis the IP address andw.x.y.zis the subnet mask.
Note: In this example,vswif0is the Service Console adapter that is the interface to which you are applying the IP address change.
- Open the
/etc/hostsfile with a text editor and modify it so that it reflects the correct IP address and hostname.
Note: You may also need to verify and change the file /etc/vmware/esx.conf file for the hostname and IP address.
- To change the default gateway address and the hostname, edit the
/etc/sysconfig/networkfile and change the GATEWAY and HOSTNAME parameters to the proper values. - For the changes to take place, restart the network service with the command:
[root@server root]#service network restart
Note: If you are required to edit the hostname, then you must reboot the host.
Note: This command breaks any current network connections to the Service Console, but virtual machines continue to have network connection. If the ESX host is managed by VirtualCenter or vCenter Server, you may have to remove and re-add the host to the inventory. For more information, see ESX not working properly in VirtualCenter after IP address change (1005633).
Note: If the changed IP does not persist across a reboot, try deleting and recreating the Service Console vswif management interface. For more information, see Recreating Service Console networking from the command line (1000266).
Changing the hostname without rebooting
To dynamically change the hostname, run the command:[root@server root]# hostname newnameNote: This command creates a temporary hostname change. This change is lost when the system is rebooted.
Changing the DNS server settings
To change the DNS server settings, update the nameserver IPs and search domain in the/etc/resolv.conf file.Changing settings in VMware vSphere or Infrastructure Client
To change the hostname, domain, DNS servers, and default gateway in VMware vSphere or Infrastructure Client:- Highlight the ESX host and click the Configuration tab.
- Click DNS and Routing.
- Click Properties.
- To change the hostname, domain, and DNS servers, click the DNS Configuration tab and enter the appropriate values.
Note: Disable VMware High Availability if you do not want virtual machines to failover during the hostname IP change.
- To change the default gateway, click the Routing tab and enter the appropriate value.
- Reboot the ESX host for the changes to take effect .
- Reconnect the ESX host to vCenter Server with the new IP address.
Generating new certificates for the ESX host
The ESX host generates certificates the first time the system is started. Under certain circumstances, it might be required to force the host to generate new certificates. Typically new certificates only need to be generated if the hostname has been changed or the certificates have been deleted accidentally.Each time you restart the vmware-hostd process, the mgmt-vmware script searches for existing certificate files (
rui.crt and rui.key). If the files cannot be found, new certificate files are generated.To generate new certificates:
- Put the host into Maintenance Mode.
- In the directory
/etc/vmware/ssl, back up any existing certificates by renaming them with these commands:[root@server root]# mv /etc/vmware/ssl/rui.crt /etc/vmware/ssl/orig.rui.crt
[root@server root]# mv /etc/vmware/ssl/rui.key /etc/vmware/ssl/orig.rui.key
Note: If you are regenerating certificates because you accidentally deleted them, you do not have to rename them.
- Reboot your host to allow it to begin using the new certificate, or restart the host services:
- Restart hostd, using this command:
service mgmt-vmware restart
- Restart vmkauthd, using this command:
service vmware-vmkauthd restart
- Restart hostd, using this command:
- Exit Maintenance Mode.
- Confirm that the ESX host successfully generated new
certificates by running this command and comparing the time stamps of
the new certificate files with
orig.rui.crtandorig.rui.key:[root@server root]# ls -la /etc/vmware/ssl/rui*
- Disable VMware High Availability if you do not want virtual machines to failover during the hostname IP change. If you are using vSphere 4.x you can just disable host monitoring in the HA settings.
- For related information, see Verifying ESX host networking configuration on the service console (1003796).
- You may be required to regenerate your SSL certificate. For more information, see Replacing or Regenerating an SSL Certificate for the Management Interface (1843).
- You are required to edit files on an ESX host. For more information, see Editing files on an ESX host using vi or nano (1020302).
- For information on replacing VirtualCenter Server certificates, see:
- The iSCSI Qualified Name used for iSCSI storage configuration is based on the hostname of the ESX host. If you change the hostname of the ESX host, ensure to review your iSCSI software initiator configuration. For more information on iSCSI troubleshooting, see Configuring and troubleshooting basic software iSCSI setup (1008083).
- For more information on changing the hostname, see Changing the name of an ESX or ESXi host (1010821).
Thứ Hai, 23 tháng 7, 2012
SQLDMO has not been registered, please re-run SQL Server setup and contact your system administrator
Question:
When I running the Microsoft sql server enterprise manager, it raise an error of "SQLDMO has not been registered, please re-run SQL Server setup and contact your system administrator." What is the problem. My sql server has already been installed and it runs very well until today.
When I running the Microsoft sql server enterprise manager, it raise an error of "SQLDMO has not been registered, please re-run SQL Server setup and contact your system administrator." What is the problem. My sql server has already been installed and it runs very well until today.
Answer:
To solve this problem is an easy way. That is, at the Command prompt, run this command line: regsvr32 sqldmo.dll. Well, notice that if the command can not be successfully executed, then you might have to switch to the folder (use command 'cd') where the dll file lives.
To solve this problem is an easy way. That is, at the Command prompt, run this command line: regsvr32 sqldmo.dll. Well, notice that if the command can not be successfully executed, then you might have to switch to the folder (use command 'cd') where the dll file lives.
Note: SQLDMO.dll was released along with the
SQL Server2000. SQLDMO.dll is a COM object. SQLDMO is an SQL
Distributed Management Objects, also an SQL Distributed Management
Objects. It package the database objects of Microsoft SQL Server 2000.
SQL-DMO support an Automation or COM-language applications to manage all
parts of the SQL Server installation. SQL-DMO is the application
programming interface(API) used by SQL Server Enterprise Manager.
Therefore, using an SQL-DMO application can perform all the functions
that SQL Server Enterprise Manager could perform.
Thứ Hai, 9 tháng 7, 2012
FIX: Error message when you try to install SQL Server 2000: "Unable to validate product key"
Warning
Serious problems might occur if you modify the registry incorrectly by
using Registry Editor or by using another method. These problems might
require that you reinstall your operating system. Microsoft cannot
guarantee that these problems can be solved. Modify the registry at your
own risk.
To resolve this problem, follow these steps:
To resolve this problem, follow these steps:
- In the SQL Server Installation Wizard, click Cancel.
- Start Registry Editor. To do this, click Start, click Run, type regedt32, and then click OK.
- Locate and then double-click the SafeDllSearchMode registry entry.
On a server that is running Windows Server 2003 or Windows Storage Server 2003, this registry entry is located under the following registry subkey:On a server that is running Windows 2000 with SP4, this registry entry is located under the following registry subkey:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session ManagerNote If the SafeDllSearchMode registry entry does not exist, create the SafeDllSearchMode registry entry as the DWORD value.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\Control\Session Manager - In the Value data box, change the value from 1 to 0, and then click OK.
- Exit Registry Editor.
- Reinstall SQL Server 2000, and then install the latest SQL Server 2000 service pack.
- Restart the server.
Đăng ký:
Bài đăng (Atom)